
7 Viscerocranium1 ( Maxilla) YouTube
Bones of the Skull. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. It is comprised of many bones, which are formed by intramembranous ossification, and joined by sutures (fibrous joints). The bones of the skull can be considered as two groups: those of the cranium (which consist of the cranial.

VISCEROCRANIUM INDEX A total of 55 items Maxillae Alveolar process of maxilla (Figure 1
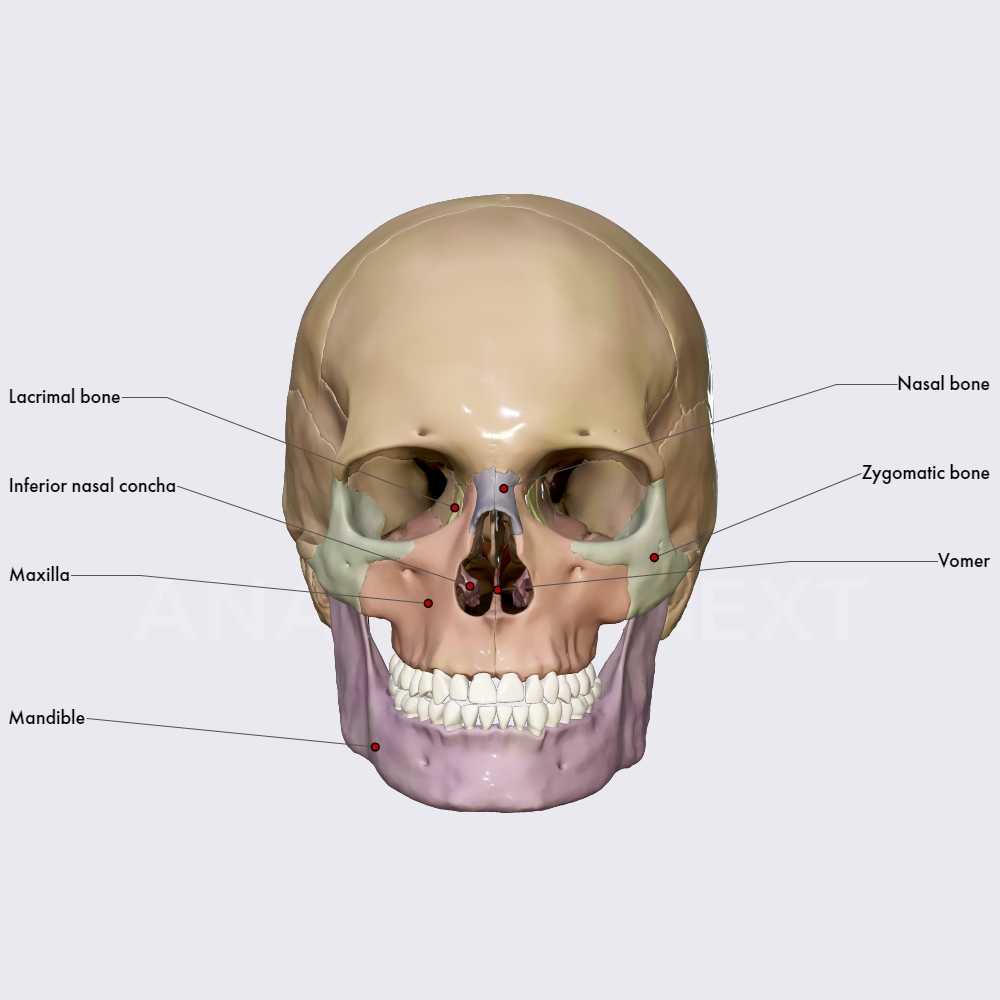
The 14 bones forming the viscerocranium are the lacrimal bones (2), nasal bones (2), zygomatic bones (2), palatine bones (2), maxillary bones or maxillae (2), inferior nasal concha, vomer, and the mandible.. In some cases, the unpaired hyoid bone is also classified as part of the viscerocranium, although located in the upper neck region. It is connected to the skull with the help of ligaments.

The Skull Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Viscerocranium. Skull (ventral view) The first part of the skull to be discussed is the viscerocranium or bones of the face. Below, they are grouped according to their derivative germ layer, their origins, their adult location and their way of ossifying. All the bones in this category are derived from cells of the neural crest.

Viscerocranium Athena Hub Workspaces Medical Harbour
The human skull is composed of two distinct parts known as the neurocranium and viscerocranium.. Neurocranium. The neurocranium consists of bones that surround and encase the brain and sensory organs connected to the brain. Therefore, the neurocranium is also known as the braincase.. The space found within the neurocranium is known as the cranial cavity, and the brain and meninges mostly.
Bones of the viscerocranium Skull Head and Neck Anatomy.app Learn anatomy 3D models
Introduction. The maxilla is the most important bone of the midface. It has a central location and provides structural support to the viscerocranium. It has functional and aesthetic significance as it has a fundamental role in facial architecture, separates the nasal and oral cavities, forms the upper jaw, and contains the maxillary sinus. [1] [2]

Viscerocranium Encyclopedia Anatomy.app Learn anatomy 3D models, articles, and quizzes
The term viscerocranium refers to the skull bones which contribute to the facial skeleton. Unlike the viscerocranium, those bones which surround the brain constitute the neurocranium (a.k.a. cranial cavity). Together, both viscerocranium and neurocranium, constitute the cranium.The viscerocranium is formed of several bones, some are paired, while others are unpaired. Examples of paired bones.
PPT CRANIUM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID850502
Introduction. The cranium (from the Greek word krania, meaning skull) is the most cephalad aspect of the axial skeleton. The cranium, or skull, is composed of 22 bones anis d divided into two regions: the neurocranium (which protects the brain) and the viscerocranium (which forms the face). The skull also supports tendinous muscle attachments.
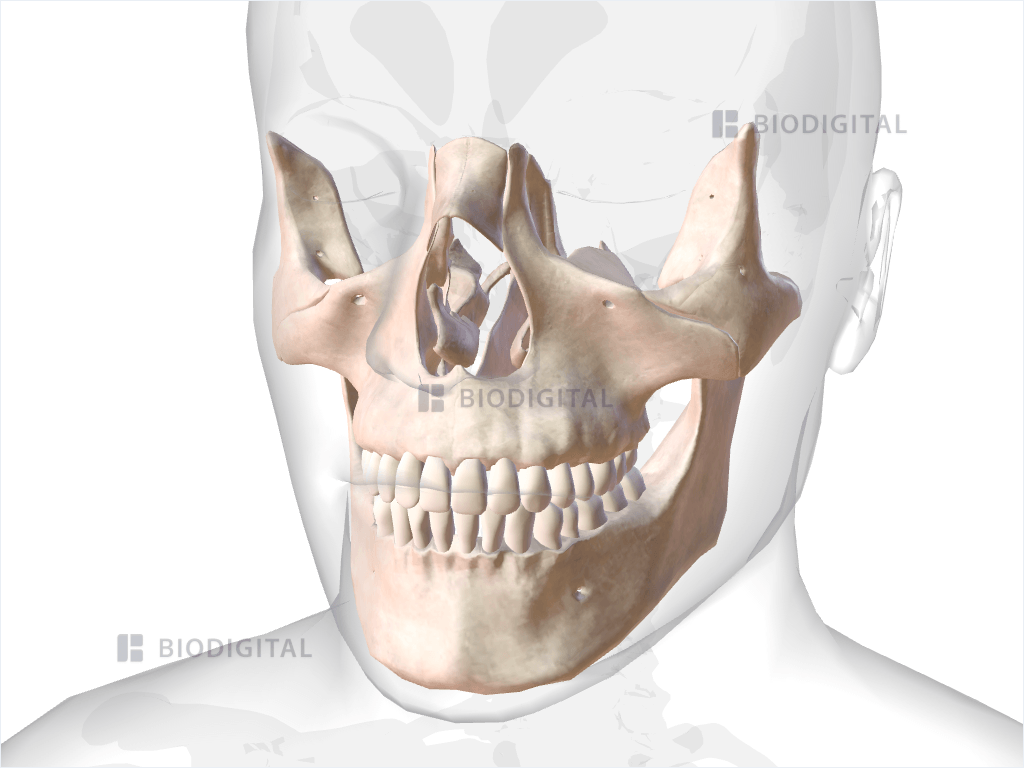
Viscerocranium BioDigital Anatomy
Want to learn all about the bones of the viscerocranium? You've come to the right place! Start learning with this video now. Once you're done watching, why n.

AnatomieCheck Viscerocranium DocCheck
The facial skeleton comprises the facial bones that may attach to build a portion of the skull. [1] The remainder of the skull is the neurocranium . In human anatomy and development, the facial skeleton is sometimes called the membranous viscerocranium, which comprises the mandible and dermatocranial elements that are not part of the braincase.
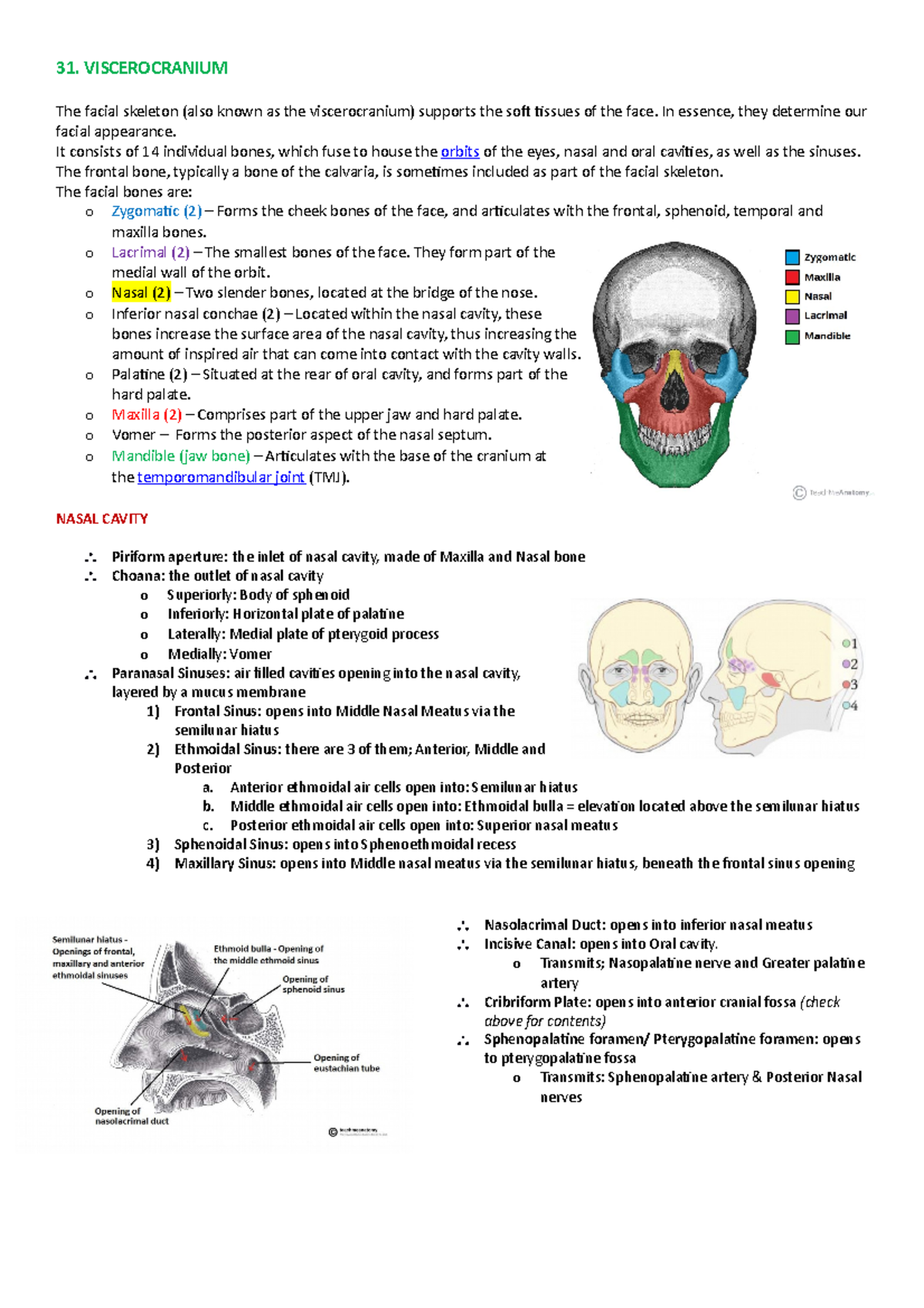
Viscerocranium and its contents 31. VISCEROCRANIUM The facial skeleton (also known as the
2. Development and Developmental Origins of the Cranial Base—The Mouse and Chick as a Template. Although described in exquisite detail elsewhere [], briefly, the cartilage anlage of the cranial base (a subset of the chondrocranium) is composed of 14 paired cartilage elements—developing near the viscerocranium and calvaria (Figure 3 A).These cartilage elements follow a genetically.

Maxilla. Lateral view Anatomy bones, Human anatomy and physiology, Skull anatomy
Viscerocranium may refer to one of two related concepts: . In human anatomy and development, viscerocranium usually refers to elements of the skull that are not part of the braincase (as opposed to the neurocranium), and which can be subdivided into: . The membranous viscerocranium, comprising the facial skeleton; The cartilaginous viscerocranium, comprising the splanchnocranium

Anatomy Standard Drawing Bones of viscerocranium anterior view no labels AnatomyTOOL
The viscerocranium is the part of the skull that is situated anterior to the neurocranium. It defines the facial skeleton and supports the soft tissue of the face. It is formed by fourteen bones, excluding the hyoid bone. Check it out. Previous slide 16 / 37. Skull (overview)

Anterior view of skull viscerocranium Diagram Quizlet
Viscerocranium: the bottom part of the skull that makes up the face and lower jaw. Chondrocranium or cartilaginous neurocranium: so-called because this area of bone is formed from cartilage (endochondral ossification). More descriptive terms include skull base and cranial floor. Cranial vault, calvaria/calvarium, or skull-cap.

202 T1 Viscerocranium anterior view Diagram Quizlet
The viscerocranium consists of 14 individual bones that fuse together. However, the hyoid bone, ethmoid bone, and sphenoid bones are sometimes included in the viscerocranium. Zygomatic Bones. The two zygomatic bones form the cheeks and contribute to the orbits. They articulate with the frontal, temporal, maxilla, and sphenoid bones.

Bones of the Viscerocranium Human Anatomy Kenhub YouTube
The vomer is a small bone of the viscerocranium (or facial skeleton). It is located in the midsagittal plane of the skull, forming the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum, where it runs in an anteroinferior direction. It has horizontal projecting superior expansions of bone called the ala of the vomer (wings) and a vertical perpendicular plate, which forms the main part of the bone.
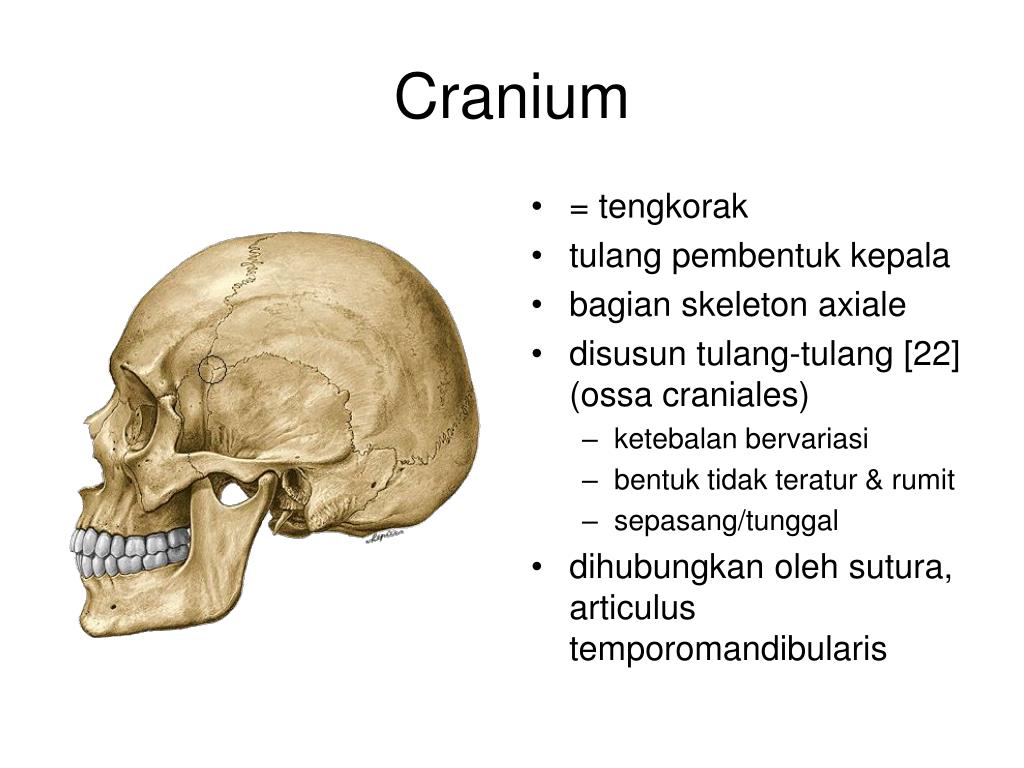
PPT CRANIUM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID850502
The neurocranium is a protective shell surrounding the brain and brain stem. The viscerocranium (or facial skeleton) is formed by the bones supporting the face. Except for the mandible, all skull bones are joined together by sutures —synarthrodial (immovable) joints. The skull contains air-filled cavities called sinuses.