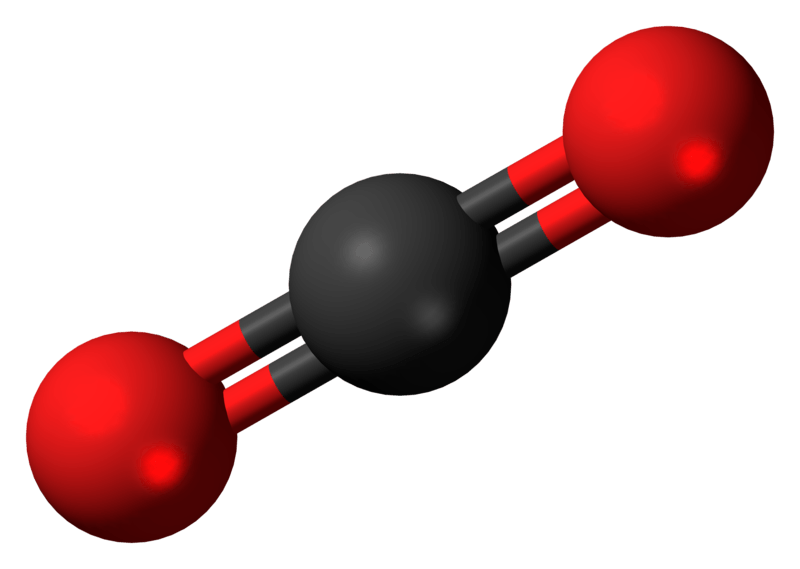
CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) Lewis Dot Structure Science Trends
Step 1: Figure out how many electrons the molecule must have, based on the number of valence electrons in each atom. When drawing the structure of an ion, be sure to add/subtract electrons to account for the charge. Step 2: Connect the atoms to each other with single bonds to form a "skeleton structure.".

CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar Mass & Hybridization
Dalam molekul NH 3 terdapat sepasang elektron yang tidak digunakan (elektron bebas) sehingga disebut Pasangan Elektron Bebas (PEB). Tiga pasang elektron yang digunakan bersama oleh atom N dan atom H disebut Pasangan Elektron Ikatan (PEI). 2. Struktur Lewis Molekul H 2 O. Atom 8 O memiliki konfigurasi elektron 8 O:2, 6.

Vector Illustration Lewis Structure Carbon Dioxide Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 2232946047
1.2.1 Lewis Structure of Diatomic Molecules. To learn about Lewis structures, we will start with the Lewis symbol. The Lewis symbol is the chemical symbol of an element with valence electrons represented as dots. The Lewis symbols of some elements are shown here: Figure 1.2a The Lewis structures of aluminum, tin, nitrogen, chlorine and bromine
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CO2LewisStructure-591c94063df78cf5fadfde77.png)
Lewis Structure Definition and Example
These electrons push away the bonded pairs of electrons,giving it its "V shape". In the case of carbon dioxide,however,the carbon atom has no lone pairs so there is no repulsion between the bonded pairs and lone pairs. For the second part of your question, the electrons are present in a 3D region around the nucleus of an atom.
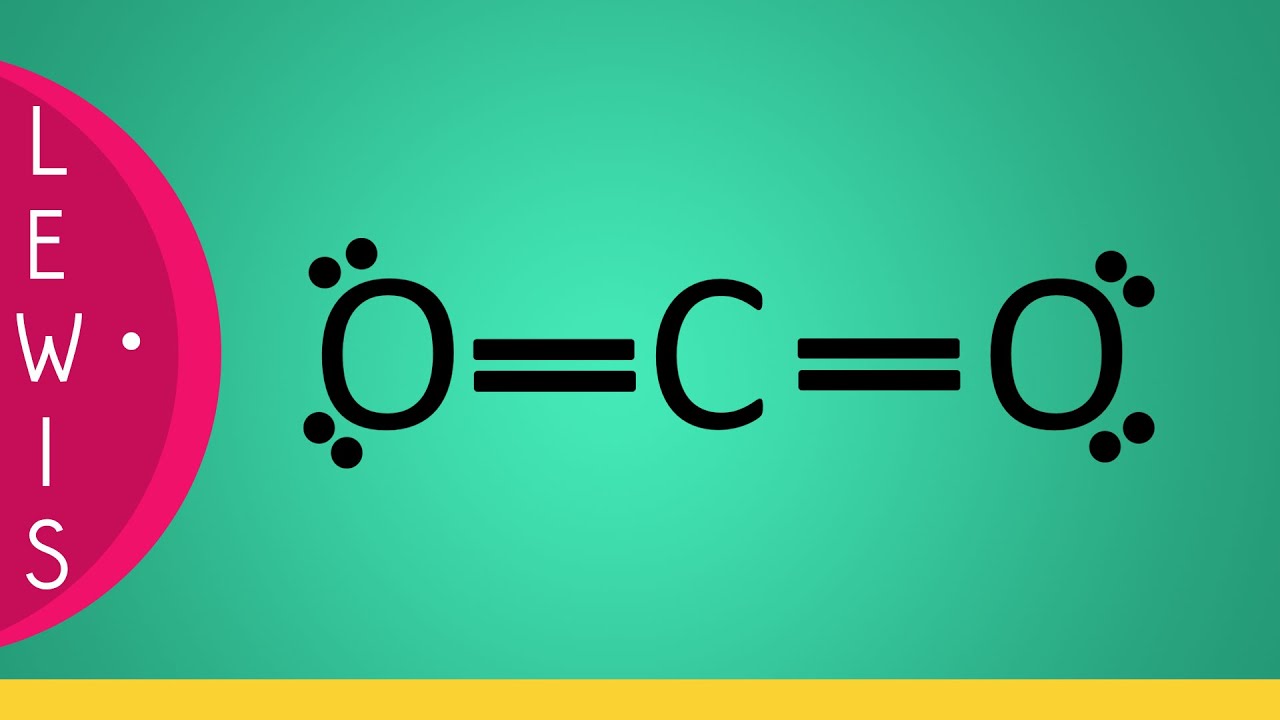
CO2 Lewis Structure YouTube
Therefore it is put in the center of the dot structure. For the CO 2 Lewis structure there are a total of 16 valence electrons available. Transcript: OK, this is Dr. B. We're going to do the Lewis structure for CO2, Carbon dioxide. On the periodic table, Carbon is in group 4, or 14 sometimes; and then Oxygen is in group 6 or 16.
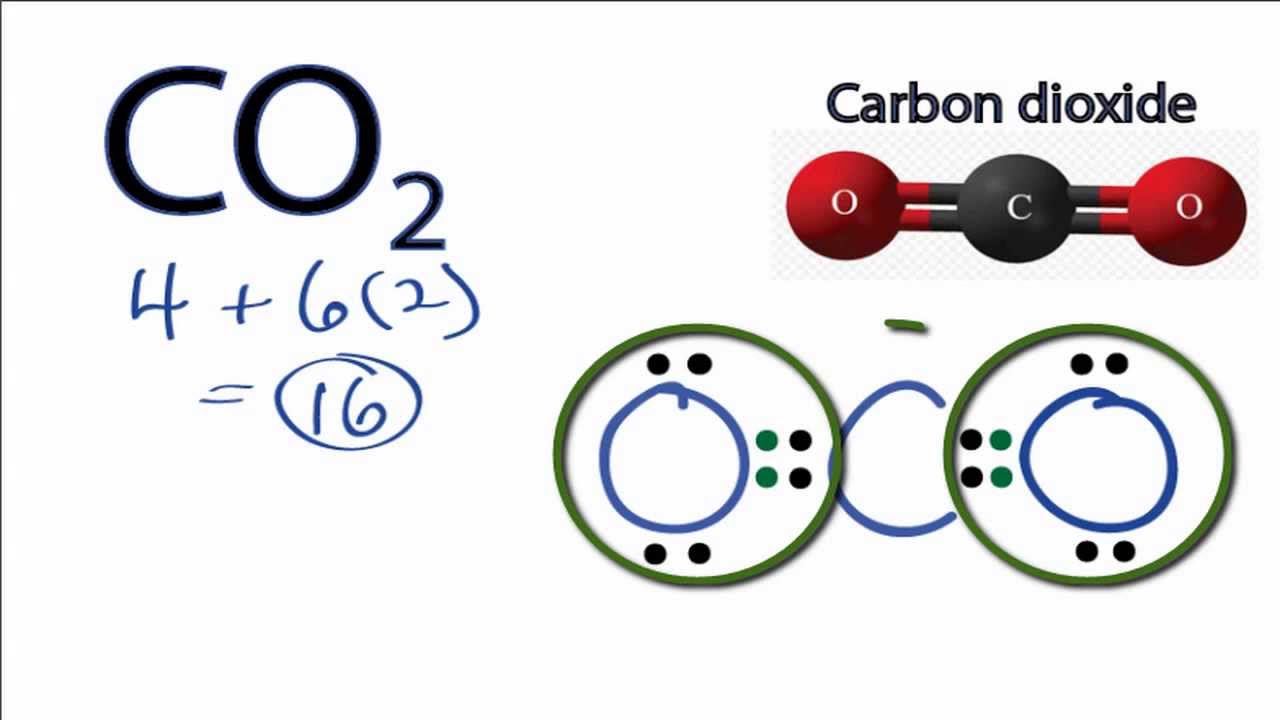
Carbon Dioxide Lewis Structure How to Draw the Lewis Structure for Carbon Dioxide YouTube
The CO 2 Lewis structure depicts the molecular arrangement of carbon dioxide, which is composed of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Within the CO 2 Lewis structure, the carbon atom is surrounded by two double bonds, with each oxygen atom attached to it. Additionally, there are two lone pairs on each oxygen atom. To draw a CO 2 Lewis structure, begin by sketching out a rough structure of.
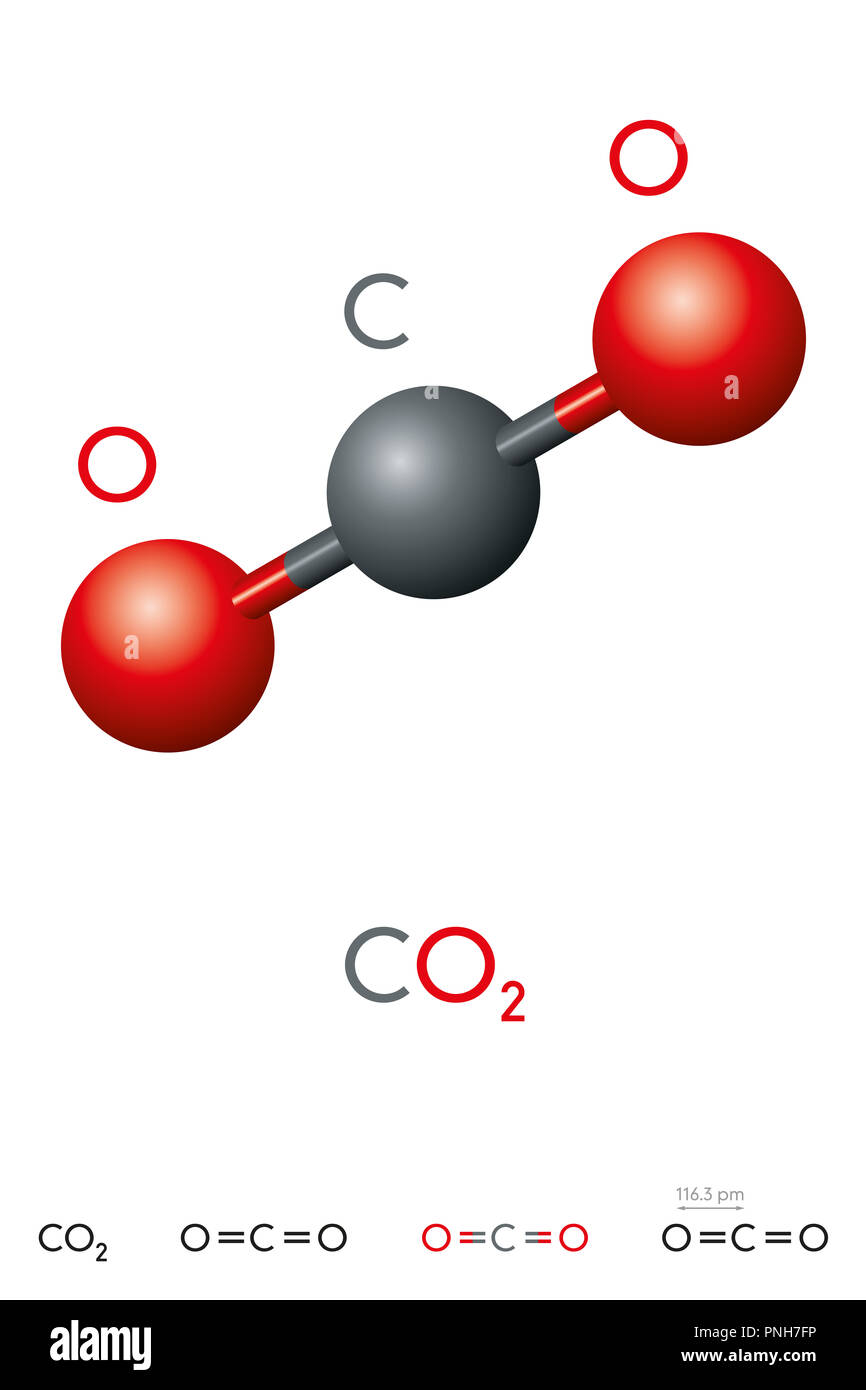
Carbon dioxide, CO2, molecule model and chemical formula. Carbonic acid gas. Colorless gas. Ball
Lewis Structures. Page ID. A Lewis Structure is a very simplified representation of the valence shell electrons in a molecule. It is used to show how the electrons are arranged around individual atoms in a molecule. Electrons are shown as "dots" or for bonding electrons as a line between the two atoms. The goal is to obtain the "best" electron.

CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry, and MO Diagram Techiescientist
Lewis structure of a water molecule. Lewis structures - also called Lewis dot formulas, Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDs) - are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. A Lewis structure can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecule, as well as.

So far, we’ve used 16 of the CO2 Lewis structure’s total 16 outermost valence shell electrons
CO2 has a linear molecular geometry with a bond angle of 180° on a plan. Molar mass of CO2 is 44.01 g/mol which is also known as molecular weight. Carbon dioxide has an sp hybridization type because the steric number of central carbon is 2. Carbon dioxide is a polar molecule but both C=O bonds are polar bonds.

MENGGAMBAR STRUKTUR LEWIS CO2BANK SOAL KE 9 YouTube
A step-by-step explanation of how to draw the CO2 Lewis Dot Structure (Carbon dioxide).For the CO2 structure use the periodic table to find the total number.

CO2 Lewis Structure, Drawing Method of CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry of CO2
The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon.

Lewis Structure Carbon Dioxide Co2 เวกเตอร์สต็อก (ปลอดค่าลิขสิทธิ์) 2109748577 Shutterstock
A green carbon capture and conversion technology offering scalability and economic viability for mitigating CO 2 emissions is reported. The technology uses suspensions of gallium liquid metal to reduce CO 2 into carbonaceous solid products and O 2 at near room temperature. The nonpolar nature of the liquid gallium interface allows the solid products to instantaneously exfoliate, hence keeping.

CO2 Lewis Structure ,Valence Electrons, Formal Charge ,Polar or Nonpolar,Octet Rule
Step #1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons. Here, the given molecule is CO2 (carbon dioxide). In order to draw the lewis structure of CO2, first of all you have to find the total number of valence electrons present in the CO2 molecule. (Valence electrons are the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom).

CO2 Lewis Structure ,Valence Electrons, Formal Charge ,Polar or Nonpolar,Octet Rule
Lewis Structure Finder. This widget gets the Lewis structure of chemical compounds. Get the free "Lewis Structure Finder" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. Find more Chemistry widgets in Wolfram|Alpha.

CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) Lewis Dot Structure Science Trends
I quickly take you through how to draw the Lewis Structure of CO2 (Carbon DiOxide). I also go over hybridization, shape and bond angles.

What is the Lewis Dot structure for CO2 (Carbon dioxide)?
Carbon dioxide is a colourless, odourless, incombustible gas produced by the combustion of carbon. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is 1:2. Two double bonds connect the carbon and oxygen atoms in the Lewis structure. Two oxygen atoms are present at the terminals, where they share electrons and form bonds with the central carbon atom.