
Pengertian Rumus Dan Cara Menghitung Odds Rasio Dalam Analisis My XXX Hot Girl
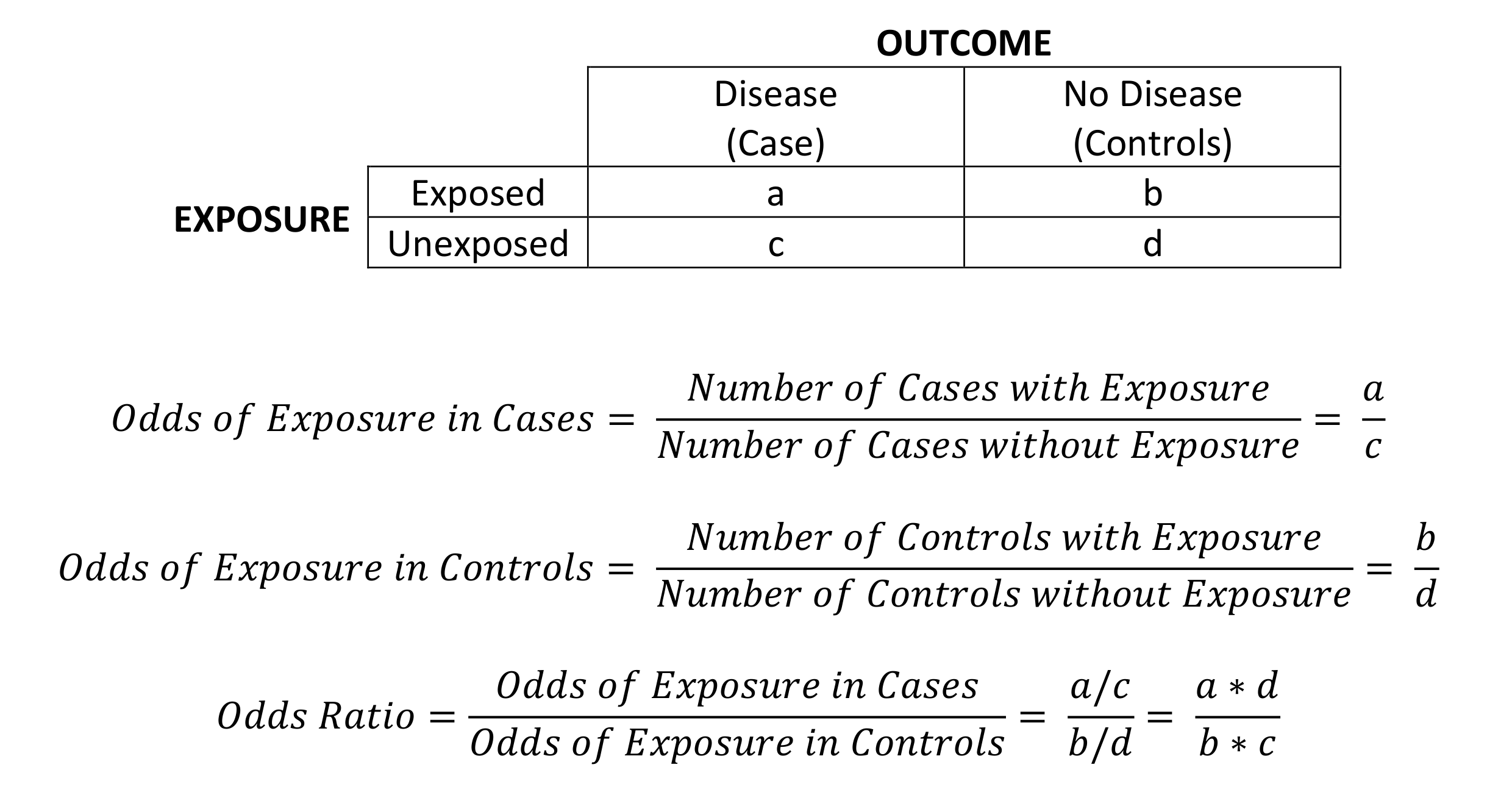
Hitung odds rasio menggunakan rumus yang telah disebutkan sebelumnya. Misalnya, jika Anda memiliki a = 100, b = 50, c = 80, dan d = 70, maka odds rasio akan menjadi ((100/50) / (80/70)) = 2. Interpretasikan hasil odds rasio. Jika nilai odds rasio adalah 1, berarti tidak ada hubungan antara variabel dependen dan independen.
Understanding Relative Risk and Odds Ratios Research
Odds = P (positive) / 1 - P (positive) = (42/90) / 1- (42/90) = (42/90) / (48/90) = 0.875. Thus, the odds ratio for experiencing a positive outcome under the new treatment compared to the existing treatment can be calculated as: Odds Ratio = 1.25 / 0.875 = 1.428. We would interpret this to mean that the odds that a patient experiences a.
PPT 16 Odds Ratios [from casecontrol studies] PowerPoint Presentation ID464336
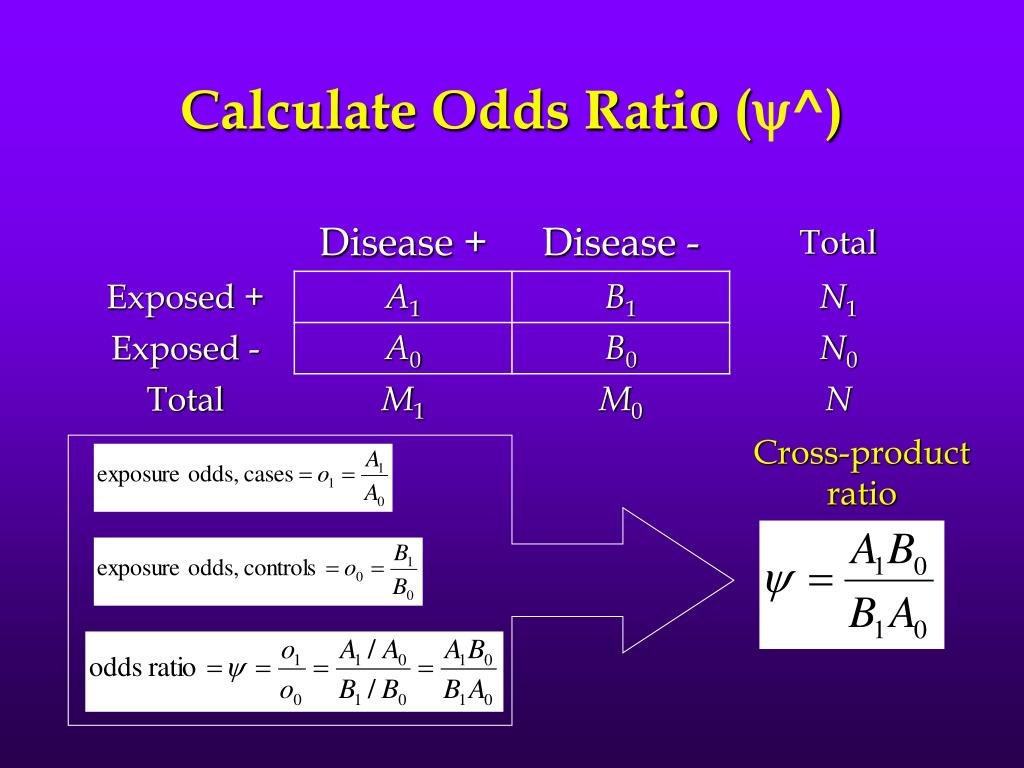
How to Calculate the Odds Ratio. Step 1: Calculate the odds that a member of the population has property "A". Assume the person already has "B.". Step 2: Calculate the odds that a member of the population has property "A". Assume the person does not have "B.". Step 3: Divide step 1 by step 2 to get the odds ratio (OR).

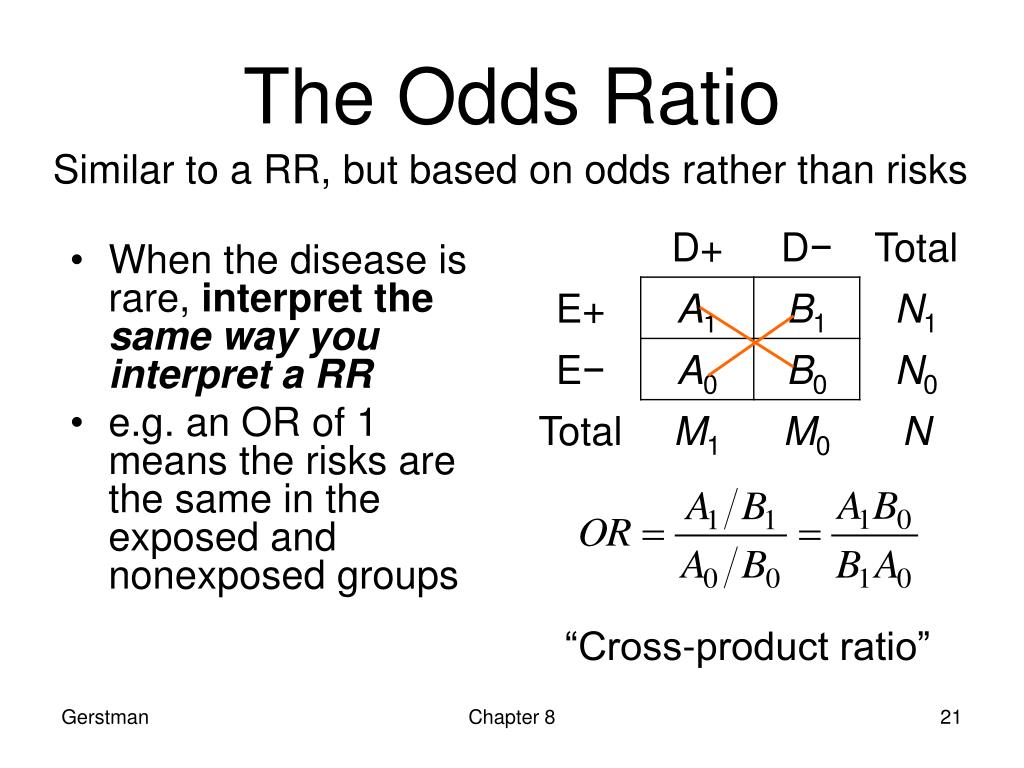
Interpretation of Odds Ratio. Odds Ratio greater than one and less than one YouTube
The Mantel-Haenszel method provides a pooled odds ratio across the strata of fourfold tables. Meta-analysis is used to investigate the combination or interaction of a group of independent studies, for example a series of fourfold tables from similar studies conducted at different centres. This StatsDirect function examines the odds ratio for.
PPT 16 Odds Ratios [from casecontrol studies] PowerPoint Presentation ID464336
The odds ratio (OR) is a simple tool, widely utilized in clinical research. As a simple statistic, it can be hand calculated to determine the odds of a particular event or a disease, and the.
PPT Epidemiology Kept Simple PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1228400
To manually calculate the odds ratio, you can use the formula: # Manual calculation of odds ratio odds_ratio <- (a * d) / (b * c) Using the fisher.test( ) function. The Fisher's Exact Test function in R can also be used to calculate the odds ratio for a 2×2 table.
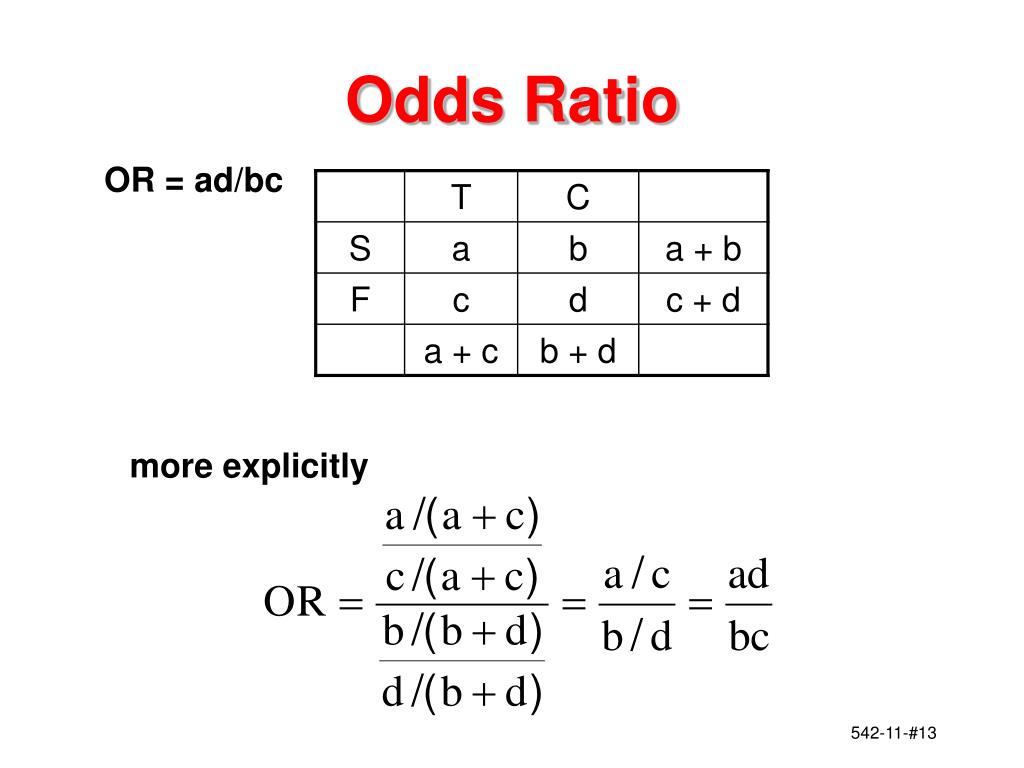
PPT Statistics 542 Introduction to Clinical Trials Meta Analysis PowerPoint Presentation ID
Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies. In cross-sectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated. However, it should be noted that.

Odds Ratio OR Kau lah segalanya Odds Ratio (OR) adalah ukuran asosiasi paparan (faktor
More specifically, the estimated odds ratio, 0.5423, with 95% confidence interval (0.4785, 0.6147) indicates that the odds of acceptance for males are about two times as high as that for females. What about this relationship viewed within a particular department? The CMH test statistic of 1.5246 with df = 1 and p-value = 0.2169 indicates that.

Wie und interpretiert man die Odds Ratio und die Risk Ratio? 💡 YouTube
The odds ratio is a statistical measurement that helps to understand the comparison of the combined effect of the parameter of each group into a single parameter scale. It is frequently used in.
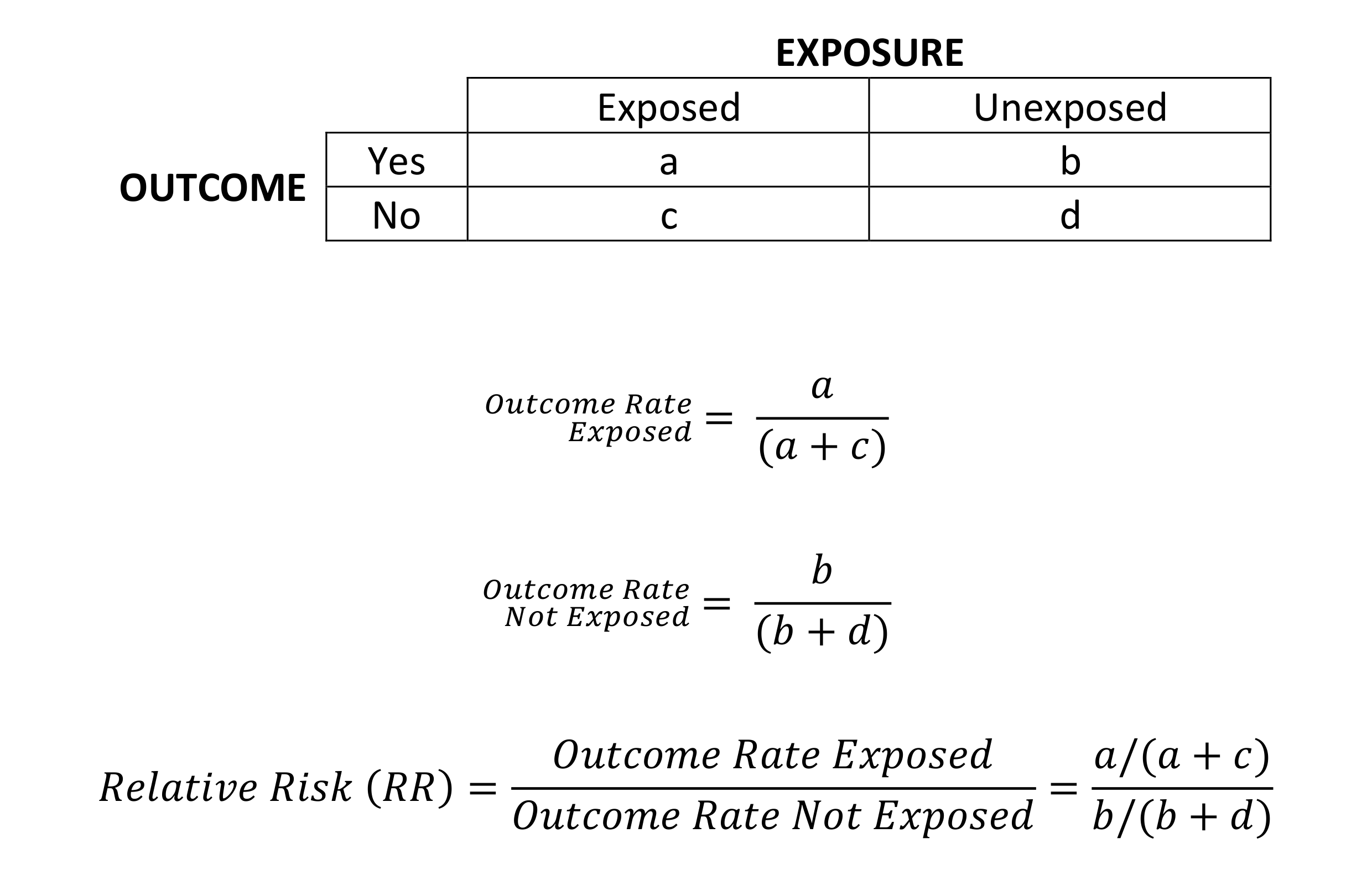
Understanding Relative Risk and Odds Ratios Research
Odds Ratio Dalam SPSS. Odds Ratio (OR) adalah ukuran asosiasi paparan (faktor risiko) dengan kejadian penyakit; dihitung dari angka kejadian penyakit pada kelompok berisiko (terpapar faktor risiko) dibanding angka kejadian penyakit pada kelompok yang tidak berisiko (tidak terpapar faktor risiko). Sebagai contoh, kita ambil sebuah kasus yaitu.
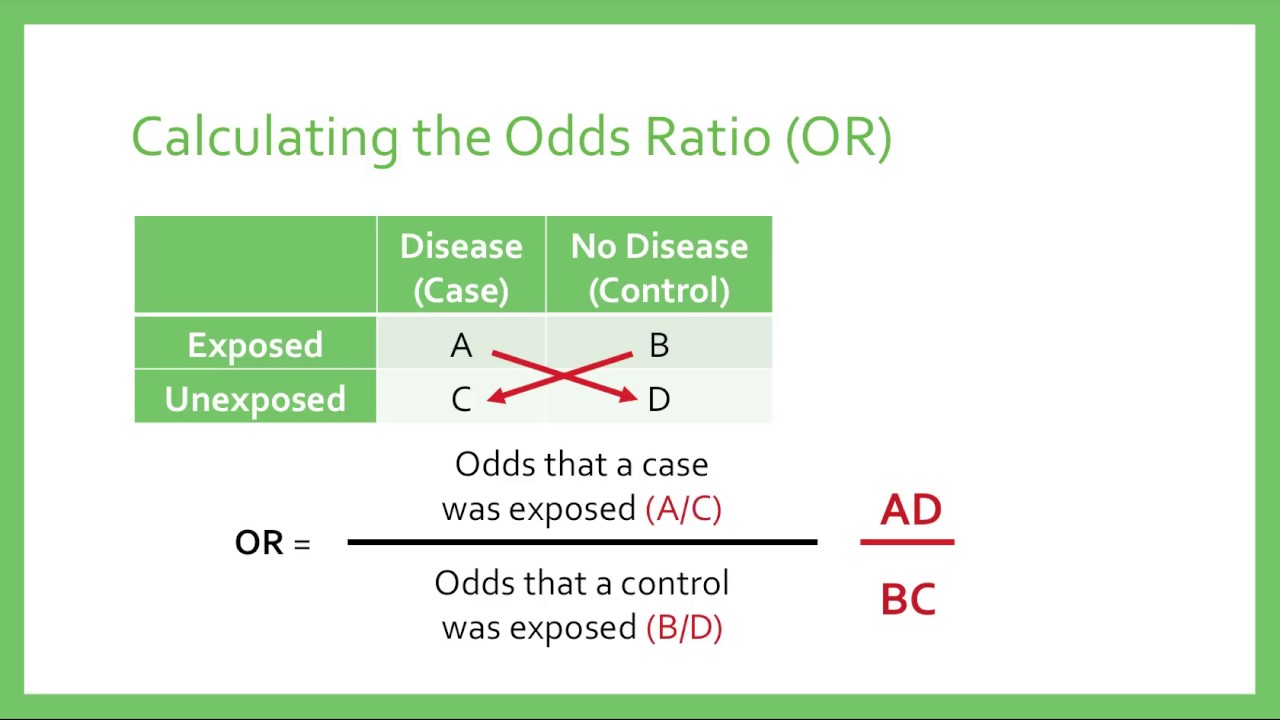
NGHIÊN CỨU ĐỊNH LƯỢNG, HỖ TRỢ NGHIÊN CỨU KHOA HỌC
For example, if a log odds estimated by logistic regression is 0.4 then the odds ratio can be derived by exponentiating the log odds (exp(0.4) = 1.5). It is the odds ratio that is usually reported in the medical literature. The odds ratio is always positive, although the estimated log odds can be positive or negative (log odds of −0.2 equals.

21+ How To Calculate The Odds Ratio Today Hutomo
The odds ratio for these data is: v u ˆOR = The confidence interval for ψ is OR e OR z SE ln ˆ ln ˆ ± ⋅ where e is the base on the natural logarithms (e ≈ 2.71828…), z is a Standard Normal deviate corresponding to the desired level of confidence (z = 1.645 for 90% confidence, z = 1.96 for 95% confidence, and z = 2.576 for 99%.

How To Calculate Odds Ratio & 95 Confidence Intervals In Excel YouTube
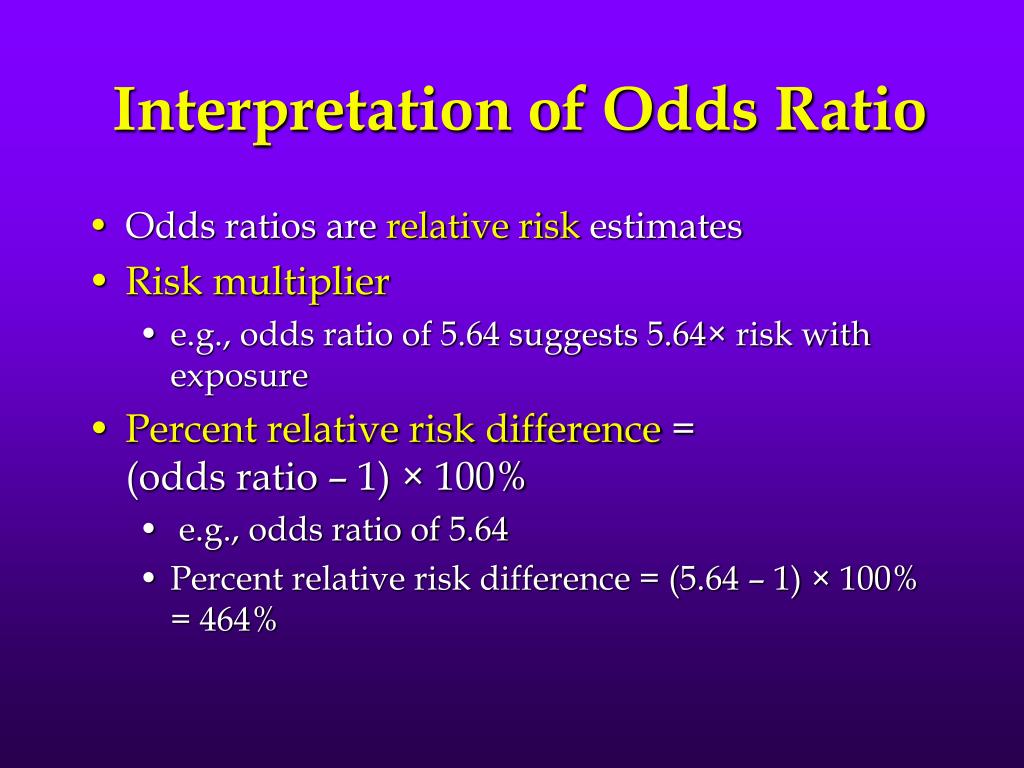
Odds Ratio = 1: The ratio equals one when the numerator and denominator are equal. This equivalence occurs when the odds of the event occurring in one condition equal the odds of it happening in the other condition. There is no association between condition and event occurrence. Odds Ratio > 1: The numerator is greater than the denominator.
4. Since the 95 confidence interval includes the null value of 1.0, it is plausible (from these
However, odds approaches risk when the risk is small. If the risk of a pulmonary embolism following a surgery is 1/100, the odds are 1/99, which is nearly the same. The general rule of thumb is that the odds approaches risk when the risk is less than 10%. Odds are not intuitive and you rarely see absolute odds in the spine research.

Cara Menghitung Odds Ratio (RO) dengan SPSS, Crosstabs, Regresi Logistik, Pada Kasus Covid19
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of A in the presence of B and the odds of A in the absence of B, or equivalently (due to symmetry), the ratio of the odds of B in the presence of A and the odds of B in the absence of A.Two events are independent if and only if the OR.

PPT Conditional Probability PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3198940
The formula can also be presented as (a × d)/ (b × c) (this is called the cross-product). The result is the same: (17 × 248) = (15656/4216) = 3.71. The result of an odds ratio is interpreted as follows: The patients who received standard care died 3.71 times more often than patients treated with the new drug.